Watch the video below to learn more about Gartner’s Hype Cycle Tool
Authored by: Wasim
As a technology executive, you are constantly expected to embrace new technologies and trends to help your business gain a competitive edge in your industry. How do you make those decisions, especially when the technologies in question are still new and have a greater risk associated with their adoption?
Let’s take some recent trends. A lot of enterprises are testing the waters to potentially adopt emerging technologies such as machine learning, smart robots, cognitive computing, etc. How can one get a perspective on the maturity of these technologies within enterprises in general and their future potential?
To help with these decisions, Gartner introduced its Hype Cycle tool a few years ago and is currently used by many organizations to drive their technology strategy and investment decisions. The Hype Cycle is a graphical representation of how technologies progress from conception to maturity to becoming mainstream. This tool helps technology professionals get insights on the maturity levels of various technology innovations and the market adoption path that a technology may take in the future.
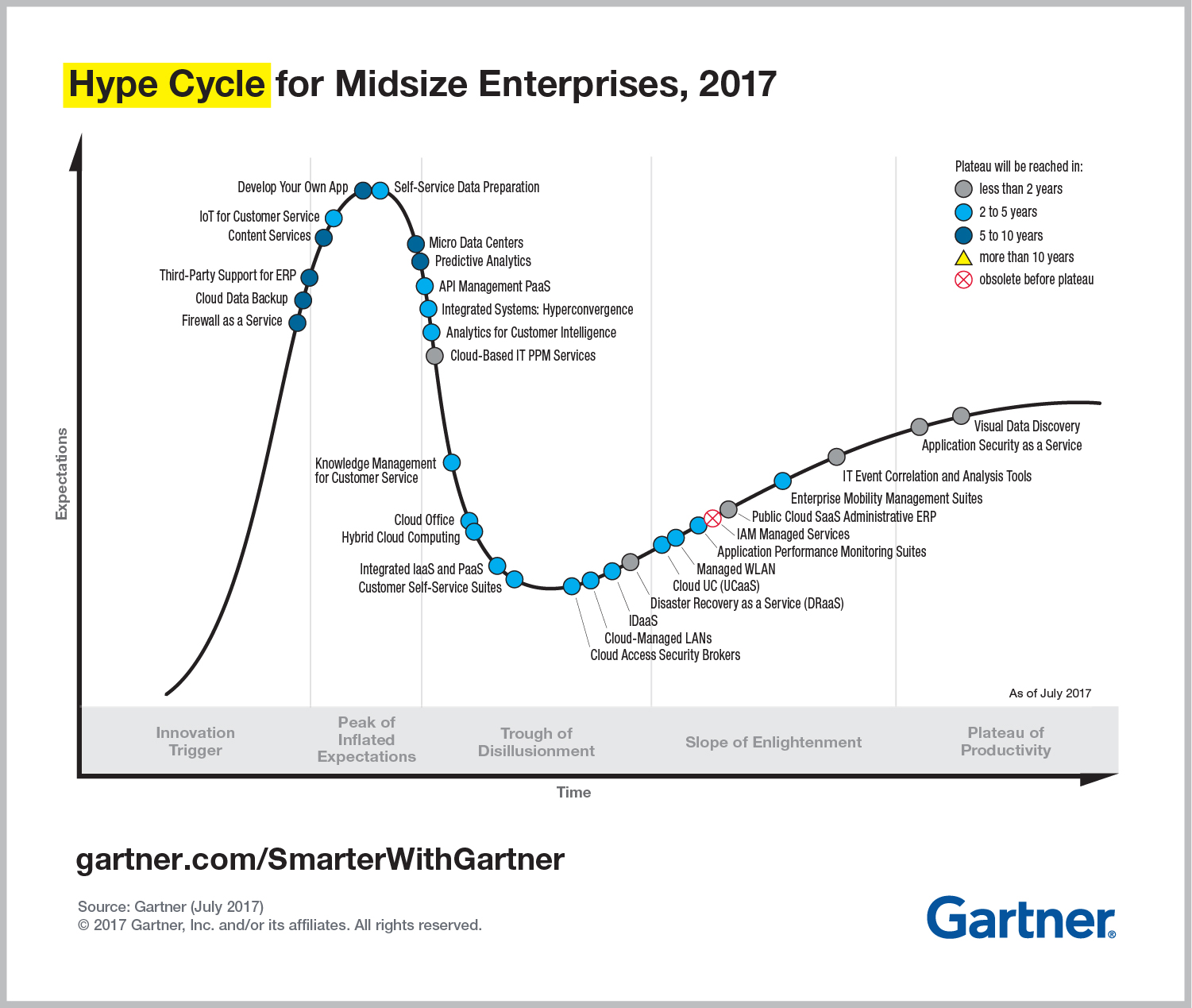
Each year, Gartner releases more than 90+ Hype Cycles related to various domains. Some of the recently released Hype Cycles relate to domains, such as Emerging Technologies, Midsize Enterprises, Data Management, Digital marketing and advertising, Internet of Things (IoT), and others. An example of a Hype Cycle diagram is included below in this article. You should note that the diagram is included as part of a detailed report that Gartner issues to its members only and is not available in the public domain.
The Five Phases of the Hype Cycle
The Hype cycle (presented below) is a graphical representation that shows a new technology’s progression through five distinct phases before reaching a ‘plateau of productivity’, where it is considered mature and mainstream. The Innovation Trigger is the first phase, when a technology breakthrough creates early excitement in the market and starts to become popular. At this phase, the adoption amongst a select few early adopter organizations picks up pace. However, the products related to the technologies in this phase are still not mature and are not widespread.
The technology then reaches the next phase of Peak of Inflated Expectations, where the market’s expectations peak, and the market slowly starts to lose interest, perhaps due to the technology not living up to the hype or other reasons. As Gartner states, the only enterprises making money in this phase are conference organizers and magazine publishers. From here, due to lack of meaningful results and accompanying negative coverage, the interest and adoption slow considerably, and the technology slides down and hits the Trough of Disillusionment. Although one would think that most technologies would die in the trough, an interesting thing happens, and the interest in certain technologies starts to pick up again. This may be due to focused experimentation by some organizations that leads to a true understanding of the technology’s applicability. This is where the technology enters the phase known on the Hype Cycle as Slope of Enlightenment. From here, the benefits of the technology are widely understood, tools mature in the market, and the use of technology stabilizes and enters the phase of Plateau of Productivity.
The Use of the Hype Cycle Tool
The Hype Cycle is a useful tool, as it can help technology managers get an informed perspective before rushing to adopt new innovations or abandoning them as those technologies fail to live up to earlier touted expectations. In general, the tool can help technology executives get a perspective on the following:
- For a given technology domain, the Hype Cycle shows multiple technologies (or items) providing a good overview of the overall domain. In many cases, this may expose managers to other innovations that may be more relevant to them and that they had not known earlier. For example, in the figure below, Gartner’s Hype Cycle for data management shows 30+ technologies.
- Understanding the maturity state of technologies and other items on the Hype Cycle graph (emerging, adolescent etc.)
- Reasons for which a technology is in a certain phase
- Market penetration levels of the technology within the target audience
- Technologies highlighted in earlier years in the Hype Cycle that may be going obsolete. Although there are no rules when this can happen during the Hype Cycle, this usually happens within the first three phases before it reaches the scope of enlightenment phase.
- Timeframe before certain technologies are expected to become mainstream
- Level of risk that may be associated with adopting certain technologies (depending on their position on the Hype Cycle).
Observations
The following delineate some observations related to the use of this tool.
- For a technology to be in the trough of disillusionment doesn’t indicate that a technology may necessarily overcome the barriers and progress to the next phase, nor does it mean it will die in that phase.
- The duration that a technology may take to progress from one phase to another varies by technology.
- For technologies that are identified in the early phases of the cycle and highlighted to reach the plateau of productivity phase within a short time span, this may be taken as Gartner’s high confidence in the technology to become mainstream quickly. As a decision maker, this can provide you the confidence of piloting and investing in the implementation of those technologies.
- It’s possible that a technology may become successful without hitting the trough of disillusionment, even though some argue that technologies rarely mature before going through a disillusionment phase.
Limitations
The following are some perceived limitations related to this tool.
- The Hype Cycle report is usually industry agnostic. However, in reality, certain technologies may do better in some industries than others. While the tool can provide the right perspective and enough information to put us in the right direction, we should also look at this data by considering the industry to which our organizations belong. For example, while the ‘blockchain’ technology may be an excellent technology to trial for organizations belonging to the financial industry, others may decide to wait longer to try its benefits. This is also evidenced by the fact that most ongoing trials related to blockchain are within the financial industry. Furthermore, as an organization, you should formulate a technology selection methodology that takes into consideration factors specific to your industry.
- The Hype cycle doesn’t provide detailed information on vendors offering products related to the various technologies. For that, organizations should consider reviewing Gartner’s Magic Quadrant tool that can help organizations assess potential suppliers and understand the competition and respective positioning.
Summary
In summary, let’s remember that while adopting newer technologies and innovations provide opportunities for competitive advantage and positioning, they have certain risks. Although tools such as Gartner’s Hype Cycle can provide useful insights related to new and emerging technologies, organizations should also review industry specific implementations before making strategic technology decisions.
— End
Download books on “Gartner Hype Cycle”
Podcast: Play in new window | Download
Subscribe: RSS
